You care about getting the retail delivery process right because you know every delivery carries the weight of your customer’s trust. Without a good delivery reputation you might fail to attract more customers.
Whether you’re a small business owner or a logistics professional, understanding the ins and outs of retail delivery is essential.
The Power of Retail
Retail delivery has become the backbone of modern commerce. As consumer expectations rise, so does the demand for faster, more reliable delivery services.
According to Statista, the retail delivery market in Australia is expected to see a “significant increase in revenue.”
But what exactly goes into retail delivery?
How do products get from the retailer’s shelves to the customer’s doorstep?
In this guide, we’ll explore the entire retail delivery process, breaking down each step to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of how it all works.
This guide will walk you through every aspect of retail delivery, from order processing to last-mile logistics, helping you optimize your operations for success.

What is Retail Delivery
Retail delivery services refers to the process of transporting goods from a retailer to the end customer. This can involve various stages, including order processing, packaging, shipping, and last-mile delivery.
What makes retail delivery different from other delivery types?
Five distinct factors set retail delivery services apart from delivering construction materials to a building site or food during dinner time.
Customer Expectations
Retail customers often expect fast, reliable delivery and expect local retailers to offer same day delivery, making speed and accuracy critical. This contrasts with business-to-business deliveries, where timing might be more flexible.
High Volume and Frequency
Retail deliveries typically involve a high volume of orders, often with smaller package sizes. This necessitates efficient order processing and logistics systems that can handle frequent shipments.
Last-Mile Complexity
Last-mile delivery in retail is more complex due to the need to deliver directly to consumers’ homes.
Therefore, it is more complex to navigate residential areas without route-optimizing software to coordinate the delivery times. It requires software to enable feedback from a customer on whether the person is available to receive packages.

Reverse Logistics
Retail delivery often involves a higher rate of returns, requiring a robust system for handling reverse logistics, such as processing returns, restocking items, and refunding customers.
The key component of reverse logistics is to recoup value from the item or dispose of it and maintain repeat business.
Diverse Delivery Options
Retailers offer various delivery options, such as same-day delivery, next-day, click-and-collect, or store-to-door services. These cater to customers’ diverse preferences and add layers of complexity to logistics planning.
Types of Retail Delivery
Direct-to-Consumer (D2C)
Products are shipped directly from the retailer to customers, from the door of the supplier to the door of the receiver.
Benefits of D2C
- Retail businesses can serve customers in remote or rural areas with home delivery.
- Retail businesses can maintain more control over the delivery experience.
- They can offer various delivery slots or express delivery options.

Downside of D2D
- Door-to-consumer delivery can be expensive.
- If a customer is not available to receive the package, delivery attempts may fail.
Store-to-Door
Customers place orders online or in a physical store, and the items are delivered from the nearest retail location.
Benefits of store-to-door
- Retailers can leverage existing store stock, reducing the need for additional storage.
- There is also potential for same day delivery or next-day delivery.
Downside of store-to-door
- Managing inventory across multiple stores can be challenging.
- Coordinating deliveries from multiple store locations adds complexity to logistics.
- Not all items may be available at every store location.
Dropshipping
Retailers don’t hold inventory; instead, they pass orders to third-party suppliers who ship directly to customers.
Benefits of dropshipping
- Dropshipping allows retailers to start selling without needing to purchase or hold inventory.
- Since retailers don’t need to physically stock items, they can offer a broader range of products.
- Dropshipping is also easily scalable, as there are no concerns over the logistics.
Downside of dropshipping
- Retailers have little to no control over the inventory, packaging, and shipping processes.
- They have zero customer engagement.
- Since retailers don’t manage their inventory, they may face problems with stock availability.

The Order Process
There are three key processes in the order process.
- Order placement
- Order verification
- Order fulfillment
Let’s look at each component and how it fits into the bigger picture.
Order Placement
The retail delivery process begins when a customer places an order, either online, via an app, or in-store.
Accurate order management systems are crucial here to ensure details are correctly captured. Details that will be captured include shipping address and payment information.
Order Verification
Once an order is placed, the retailer verifies stock availability, payment details, and delivery addresses. It’s also important to verify whether the payment was successful.
During this step, the shipping information will also be verified to ensure it’s complete and items are available in stock. This step is critical to avoid errors and fraud and ensure a smooth delivery process.
Order Fulfillment
After verification, the order moves to the fulfillment stage, where it is picked, packed, and prepared for shipment. It has to be labeled for shipment before it’s handed over to the delivery service.
Efficient warehouse management systems play a key role in speeding up this process.

Packaging and Shipping
Following the order process, the next phase is packing and preparing for shipping. Certain checks and balances need to be done before the item can be shipped, from choosing the right packaging to the best shipping methods.
Choosing Right Packaging
Sturdy packaging is needed to endure the long journey from the warehouse to the customer’s house to avoid a negative customer experience.
Things to consider when choosing the right packaging include:
- Quality packaging for during transit.
- Fragility and size.
- Weight of the packaging material.
At the same time, it also has to be kind to the environment.
Here’s a guide that can help you explore ideas for reusable, recycled, and compostable packaging: Creating sustainable packages for your products
Shipping Methods
There are quite a few options to consider, which are determined by two of the most important factors.
Factor One: Delivery time. How fast your customer wants the product to be delivered.
Factor Two: The costs involved. How much the customer is willing to pay the company?
For those who want speed, there is expedited shipping, overnight shipping, and priority shipping. For those tighter budgets, there are flat-rate shipping, economy shipping, and local delivery pickup.
Last-Mile Delivery for Retail
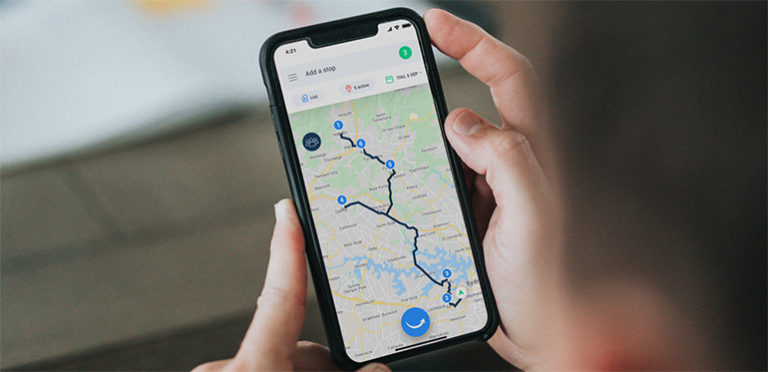
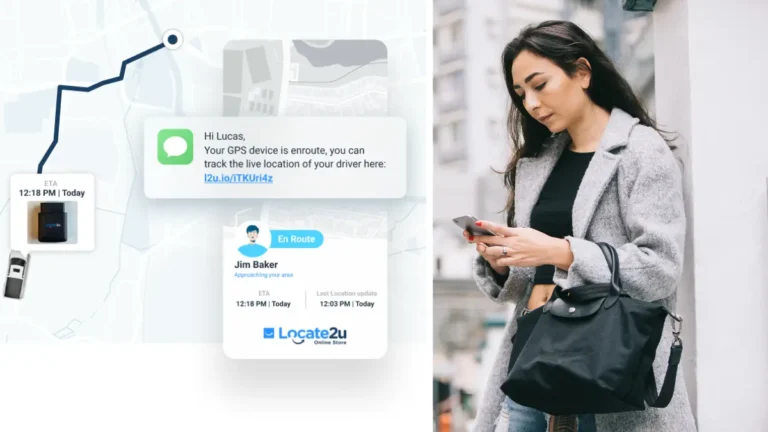
Last-mile delivery is the final leg of the delivery journey and is often referred to as the most important one. It’s the final process in which the customer has to be involved with every step. Live tracking software is important to give customers peace of mind about where the parcel is and when it can be expected to arrive.
WATCH: Choosing the right last-mile delivery software for your company requires thorough research, so here’s some help with that.
Some challenges involved in last mile delivery can slow down the process. Think of the traffic congestion in urban areas, the inaccurate address that can lead to a failed delivery, and the customer’s availability.
Luckily, there is technology to help with route optimization, taking the uncertainty out of the process, whether it is delivering goods at offices or at homes. Retailers use automated notifications to streamline the last mile and help drivers with the last step in creating a pleasant online shopping experience.

Tracking and Communication
Real time tracking updates can build trust and ensure customers order again to ensure transparency and mitigate expectations during the last mile. Customers want to know the delivery time, day delivery expectations, real time visibility, and whether drivers will be timely. It all ties into convenience and trust.
Automated notifications technology could be sent via SMS, email, or apps. Uber is one of the industry’s best examples of accurately communicating with customers.
READ MORE: How Uber delivery changed last mile delivery.
Handling Returns
A business can potentially reduce returns by improving delivery efficiency and accuracy. However, returns are an inevitable part of retail delivery. To make reverse logistics efficient, a company can process the returns quickly, restock them, and refund customers promptly.
Setting clear guidelines will ease frustration and conflict. Shopify warns that without a clear return policy, requests can “eat up a lot of time, energy, and money.”
It’s vital, especially during peak seasons like Christmas, when orders flood in and unwanted gifts are returned.
Photo credit: Canva
About the author
Mia is a multi-award-winning journalist. She has more than 14 years of experience in mainstream media. She's covered many historic moments that happened in Africa and internationally. She has a strong focus on human interest stories, to bring her readers and viewers closer to the topics at hand.