Understanding real-time tracking and GPS terminology is crucial for logistics managers.
Whether you’ve been thrown into the deep end and found yourself as a logistics manager with no experience at a startup or whether you have been at the logistics helm for years.
Understanding the real-time tracking to the core will enable a logistics manager to monitor vehicle locations, streamline routes, and enhance overall fleet performance.
With better knowledge, managers can allocate resources better and reduce the fleet’s fuel consumption.
A solid grasp of tracking concepts empowers managers to make data-driven decisions and optimize logistics operations.
Equipping managers to improve efficiency and security leads to better customer satisfaction. Consider the accuracy of the delivery estimates and timely updates.
In this article, you’ll learn about the core tech that is the backbone of real-time tracking, navigation, and positioning and how data accuracy plays a pivotal role.
What Is The Core Tech For Real-Time Tracking?
Knowing every movement of your driver, vehicle, or assets is only possible through technology like the Global Positioning System (GPS) and the broader Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS).
These systems provide precise location and time data worldwide.
Real-time tracking and telematics help businesses continuously monitor and manage shipments, trucks, and individuals while also improving security and efficiency.
Here are four core technologies behind real-time tracking.
1. Global Positioning System (GPS)
GPS is a satellite-based navigation system that provides information on global locations and times.
Nasa describes it as a network of over 30 satellites orbiting Earth. Now, these satellites continuously send out signals that allow devices like smartphones and car navigation systems to determine their exact location on the planet.
That’s how a GPS device can calculate its position, helping to navigate from one point to another.

2. Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS)
GNSS is an umbrella term for satellite navigation systems, and it offers global coverage. Although it’s invisible, millions of people rely on his technology daily.
According to Novatel, the integration of multiple GNSS constellations improves the reliability and accuracy of positioning services. This again helps to ensure that users have access to precise location information.
3. Real-time tracking
Real-time tracking is used not only in the logistics field but also by restaurants, medical companies, and even refuse removal businesses.
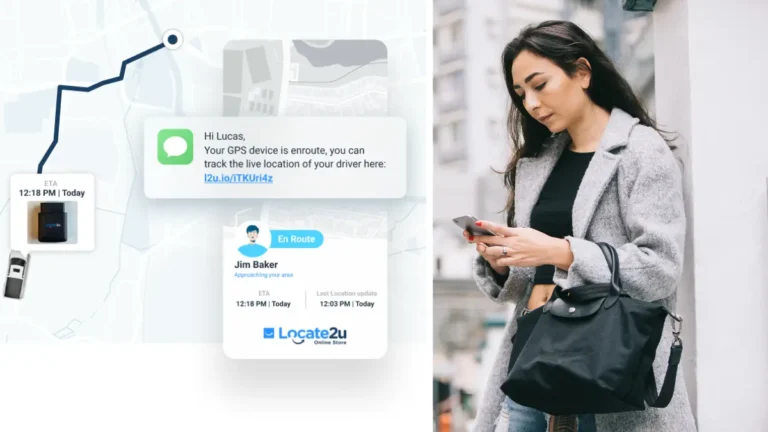
If you have customers waiting on the other end to know where you are, they better monitor their location data in real-time. A real-time tracking link provides customers or clients with information that they would not necessarily have been able to access instantaneously.
4. Telematics
Telematics uses devices installed in your fleet of vehicles to collect information like live location. It can also provide the business with information like whether the driver was speeding or how the vehicle was performing.
Telematics helps a logistics manager or fleet manager track a vehicle in real-time. It allows for quick decisions that can save time and fuel.
Why Are Navigation And Positioning Important in Tracking Assets?
For some businesses, they want to know where their expensive stock is at all times. For others, it’s about monitoring their staff and their performance. However, other companies are all about improving their customer experience through better communication.
Real-time tracking has many purposes, but understanding where your assets are at any given moment is crucial if you are running a business.
Knowing where your assets are helps you quickly respond if something goes missing or is moved without authorization.
It also has other benefits, like boosting staff efficiency. Route optimization software is a great way to use real-time location data to optimize drivers’ routes.
5. Route Optimization
Route optimization software helps improve drivers’ performance by monitoring their movement in real-time. With accurate location data, you can optimize their routes and ensure faster deliveries.
The software takes into consideration the weather conditions and traffic patterns in real time, ensuring drivers are never stuck or late.
6. Dead Reckoning
Dead reckoning is a traditional navigation technique for estimating your current position. It’s based on a previously determined location, speed, and course and advances that position based on recorded heading, speed, and time traveled.
This method does not rely on external references like GPS or landmarks. Instead, it calculates the current position by projecting from the last known point.
7. Waypoint
A waypoint is a specific geographical location that is used to help navigate and mark a point along a route or path.
In logistics, it is also called a stop. It’s defined by coordinates such as latitude and longitude, and it guides drivers to the next address. If you are using route optimization, this software will automate the process for you.
Why Do You Need Data Accuracy For Deliveries?
Missed deliveries cost companies a lot of money, money that can be spent elsewhere in the business. It means more fuel has to be used, more time goes into re-delivering to the same address, and, in the worst-case scenario – you could lose your customers.
However, if you have precise data, you can plan efficient routes and reduce fuel consumption and operational costs.
8. Assisted GPS (A-GPS)
Assisted GPS (A-GPS) is different from traditional GPS. It takes it one step further. It uses extra information from cellular networks and improves the location accuracy and speed.
When is A-GPS used? In areas where GPS signals are weak, like rural and urban areas. In urban areas, tall buildings or indoor settings can impact location accuracy and speed.
By combining satellite data with information from nearby cell towers, A-GPS provides faster and more reliable positioning.
9. Differential GPS (DGPS)
Differential GPS (DGPS) helps increase the accuracy of a standard GPS.
How does it work? It uses fixed locations equipped with high-precision GPS receivers at known locations to measure errors in GPS signals.
This method can enhance GPS accuracy from about 15 meters to less than 1 meter.
10. Inertial Navigation System (INS)
INS is a device that helps determine the location, orientation, and speed of a moving object. What makes it different is that it’s not relying on external signals like GPS.
It uses sensors called accelerometers to measure acceleration and gyroscopes to detect changes in orientation.
How to Monitoring and Managing Real-Time Tracking
Monitoring and managing your real-time tracking helps your business to optimize routes and avoid traffic congestion. It also helps with improving communication with drivers and customers.
It provides managers with information that can influence decision-making and improve overall customer satisfaction.
Here are three ways of monitoring your fleet with the help of real-time tracking software.
11. Fleet Management
Fleet management software uses GPS tracking to track the health of your vehicles or trucks in real-time. This helps you know when the vehicles need maintenance or flag any potential hazards.
Steve Orenstein, CEO and founder of Locate2u, says it can help managers solve many of their worries. “You might have different vehicles inside your business, and you want to keep track of everything that’s happening in them.
If you want to track the GPS location of the vehicle, you might also want to understand how that vehicle has been driven.”
12. Asset Tracking
Some businesses don’t necessarily want to track parcels or staff, they want to monitor their assets. One such company is WARRRL which uses real-time tracking to know where their bins are.
Asset tracking is used to monitor the location of physical assets by using GPS and real-time tracking software.
13. Geofencing
Geofencing is when you draw virtual borders around a location, place, or person. It could be the office, a warehouse, a customer, or a staff member. These virtual borders allow you to monitor when a mobile device enters or exits a geofenced area.
It can track the exact times a driver enters or leaves a delivery site. This helps businesses track movement and gather data.
READ MORE: What is geofencing and how it helps your delivery business
Technical Terms In Real-Time Tracking Simplified
Here are four technical terms used in real-time tracking, but we’ve simplified them for you.
14. Time to First Fix (TTFF)
If someone tells you the GPS can’t pick up the location due to the TTFF, you might probably panic. It stands for time to first fix. It refers to the time a GPS device takes to obtain enough satellite signals to provide accurate location information.
15. Ephemeris Data
If you need more information about satellite positions and orbits, you should request the “ephemeris data.” It is essential for accurate GPS positioning.
16. Multipath Error
Multipath error occurs when something is wrong with the GPS signals. It is caused by reflections off surfaces like buildings or terrain, which can lead to inaccurate location data.
17. Dilution of Precision (DOP)
Dilution of precision measures the geometric strength of satellite configuration. It affects the accuracy of GPS positioning.
About the author
Mia is a multi-award-winning journalist. She has more than 14 years of experience in mainstream media. She's covered many historic moments that happened in Africa and internationally. She has a strong focus on human interest stories, to bring her readers and viewers closer to the topics at hand.